
Search Results
Web results
Ultraviolet Applications: Is Really It Matters !
Note: Before We go through this article, we need to have some basics on UV Rays. If you know this then, please ignore this paragraph.
WHAT is UV Radiation?
All radiation is a form of energy, most of which is invisible to the human eye. UV radiation is only one form of radiation and it is measured on a scientific scale called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. In simplest from UV radiation is the portion of the EM spectrum between X-rays and visible light.
HOW is radiation classified on the electromagnetic spectrum?
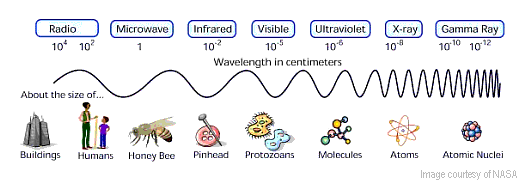
Electromagnetic radiation is all around us, though we can only see some of it. All EM radiation (also called EM energy) is made up of minute packets of energy or 'particles,' called photons, which travel in a wave-like pattern and move at the speed of light. The EM spectrum is divided into categories defined by a range of numbers. These ranges describe the activity level, or how energetic the photons are, and the size of the wavelength in each category.
[IC: NASA]
For example, at the bottom of the spectrum radio waves have photons with low energies, so their wavelengths are long with peaks that are far apart. The photons of microwaves have higher energies, followed by infrared waves, UV rays, and X-rays. At the top of the spectrum, gamma rays have photons with very high energies and short wavelengths with peaks that are close together.
 |
| Mira's(Red Giant Star 30,000 Years Ago ) bow shock and hydrogen gas tail in ultraviolet, rendered in blue-visible light. PC: Wikipedia |
Types of UV radiation?
Like all forms of light on the EM spectrum, UV radiation is classified by wavelength. Wavelength describes the distance between the peaks in a series of waves.
- UVB rays have a short wavelength that reaches the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis)
- UVA rays have a longer wavelength that can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis)
If UV radiation have on Human Body?
In humans, excessive exposure to UV radiation can result in acute and chronic harmful effects on the eye's dioptric system and retina. The risk is elevated at high altitudes and people living in high latitude areas where snow covers the ground right into early summer and sun positions even at zenith are low, are particularly at risk. Skin, the circadian system, and the immune system can also be affected.
Example:
Ultraviolet photons harm the DNA molecules of living organisms in different ways. In one common damage event, adjacent thymine bases bond with each other, instead of across the "ladder". This "thymine dimer" makes a bulge, and the distorted DNA molecule does not function properly.
Sunburn effect (as measured by the UV Index) is the product of the sunlight spectrum (radiation intensity) and the erythemal action spectrum (skin sensitivity) across the range of UV wavelengths. Sunburn production per milliwatt is increased by almost a factor of 100 between the near UVB wavelengths of 315–295 nm
The differential effects of various wavelengths of light on the human cornea and skin are sometimes called the "erythemal action spectrum".] The action spectrum shows that UVA does not cause immediate reaction, but rather UV begins to cause photokeratitis and skin redness (with lighter skinned individuals being more sensitive) at wavelengths starting near the beginning of the UVB band at 315 nm, and rapidly increasing to 300 nm. The skin and eyes are most sensitive to damage by UV at 265–275 nm, which is in the lower UVC band. At still shorter wavelengths of UV, damage continues to happen, but the overt effects are not as great with so little penetrating the atmosphere. The WHO-standard ultraviolet index is a widely publicized measurement of total strength of UV wavelengths that cause sunburn on human skin, by weighting UV exposure for action spectrum effects at a given time and location. This standard shows that most sunburn happens due to UV at wavelengths near the boundary of the UVA and UVB band.
For More Details : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultraviolet
The above paragraphs are basics which can help you to understand about UV and Types. Now we will focus on It's Application to sanitation, disinfection, and sterilization.
As COVID-19 continues to ravage global populations, the world is singularly focused on finding ways to battle the novel coronavirus. Researchers there are developing ultraviolet LEDs that have the ability to decontaminate surfaces -- and potentially air and water -- that have come in contact with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
"One major application is in medical situations -- the disinfection of personal protective equipment, surfaces, floors, within the HVAC systems, et cetera," . There is a small market already for UV-C disinfection products in medical contexts.
Indeed, much attention of late has turned to the power of ultraviolet light to inactivate the novel coronavirus. As a technology, ultraviolet light disinfection has been around for a while. And while practical, large-scale efficacy against the spread of SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be shown. UV light shows a lot of promise: SSLEEC member company Seoul Semiconductor in early April reported a "99.9% sterilization of coronavirus (COVID-19) in 30 seconds" with their UV LED products. Their technology is currently being adopted for automotive use, in UV LED lamps that sterilize the interior of unoccupied vehicles.
It's worth noting that not all UV wavelengths are alike. UV-A and UV-B -- the types we get a lot of here on Earth courtesy of the Sun -- have important uses, but the rare UV-C is the ultraviolet light of choice for purifying air and water and for inactivating microbes. These can be generated only via human-made processes.
UV-C light in the 253.76 -- 285 nm range most relevant for current disinfection technologies is also harmful to human skin, so for now it is mostly used in applications where no one is present at the time of disinfection. In fact, the World Health Organization warns against using ultraviolet disinfection lamps to sanitize hands or other areas of the skin -- even brief exposure to UV-C light can cause burns and eye damage.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic gained global momentum, materials scientists at SSLEEC were already at work advancing UV-C LED technology. This area of the electromagnetic spectrum is a relatively new frontier for solid-state lighting; UV-C light is more commonly generated via mercury vapor lamps. But now many technological advances are needed for the UV LED to reach its potential in terms of efficiency, cost, reliability and lifetime.
In a letter published in the journal ACS Photonics, the researchers reported a more elegant method for fabricating high-quality deep-ultraviolet (UV-C) LEDs that involves depositing a film of the semiconductor alloy aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN) on a substrate of silicon carbide (SiC) -- a departure from the more widely used sapphire substrate.
According to Zollner (Scientist), using silicon carbide as a substrate allows for more efficient and cost-effective growth of high-quality UV-C semiconductor material than using sapphire. This, he explained, is due to how closely the materials' atomic structures match up.
"As a general rule of thumb, the more structurally similar (in terms of atomic crystal structure) the substrate and the film are to each other, the easier it is to achieve high material quality," he said. The better the quality, the better the LED's efficiency and performance. Sapphire is dissimilar structurally, and producing material without flaws and misalignments often requires complicated additional steps. Silicon carbide is not a perfect match, Zollner said, but it enables a high quality without the need for costly, additional methods.
In addition, silicon carbide is far less expensive than the "ideal" aluminum nitride substrate, making it more mass production-friendly, according to Zollner.
Portable, fast-acting water disinfection was among the primary applications the researchers had in mind as they were developing their UV-C LED technology; the diodes' durability, reliability and small form factor would be a game changer in less developed areas of the world where clean water is not available.
The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has added another dimension. As the world races to find vaccines, therapies and cures for the disease, disinfection, decontamination and isolation are the few weapons we have to defend ourselves, and the solutions will need to be deployed worldwide. In addition to UV-C for water sanitation purposes, UV-C light could be integrated into systems that turn on when no one is present.
"This would provide a low-cost, chemical-free and convenient way to sanitize public, retail, personal and medical spaces."
UV Wavelengths and Applications:
•13.5 nm: Extreme
ultraviolet lithography
•30–200 nm: Photoionization, ultraviolet
photoelectron spectroscopy, standard integrated circuit manufacture
by photolithography
•230–365 nm:
UV-ID, label tracking, barcodes
•230–400 nm:
Optical sensors,
various instrumentation
•240–280 nm: Disinfection,
decontamination of surfaces and water (DNA absorption
has a peak at 260 nm), germicidal lamps
•200–400 nm: Forensic analysis,
drug detection
•270–360 nm: Protein analysis, DNA sequencing, drug discovery
•280–400 nm: Medical imaging of cells
•300–320 nm: Light therapy in
medicine
•300–365 nm: Curing of polymers and printer inks
•350–370 nm: Bug zappers (flies
are most attracted to light at 365 nm)
Examples of Exisitng UVC Lamp based Products:
1:
2:
3:
4:
5:
6:
7: HOW UVC AIR PURIFIER WORKS
8:
9:
10:
Source:
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/04/200414173251.htm
https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/tanning/ultraviolet-uv-radiation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultraviolet_germicidal_irradiation
https://www.mrsa-uv.com/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mira
https://www.google.com/
My Team Members
